Nature inequity and higher COVID-19 case rates in less green neighbourhoods in the United States
2021. Nature inequity and higher COVID-19 case rates in less green neighbourhoods in the United States. Nature Sustainability 4 (10).
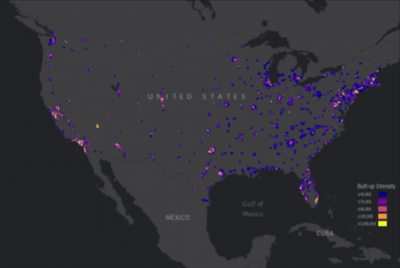 Urban nature—such as greenness and parks—can alleviate distress and provide space for safe recreation during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, nature is often less available in low-income populations and communities of colour—the same communities hardest hit by COVID-19. In analyses of two datasets, we quantified inequity in greenness and park proximity across all urbanized areas in the United States and linked greenness and park access to COVID-19 case rates for ZIP codes in 17 states. Areas with majority persons of colour had both higher case rates and less greenness. Furthermore, when controlling for sociodemographic variables, an increase of 0.1 in the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index was associated with a 4.1% decrease in COVID-19 incidence rates (95% confidence interval: 0.9–6.8%). Across the United States, block groups with lower-income and majority persons of colour are less green and have fewer parks. Our results demonstrate that the communities most impacted by COVID-19 also have the least nature nearby. Given that urban nature is associated with both human health and biodiversity, these results have far-reaching implications both during and beyond the pandemic.
Urban nature—such as greenness and parks—can alleviate distress and provide space for safe recreation during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, nature is often less available in low-income populations and communities of colour—the same communities hardest hit by COVID-19. In analyses of two datasets, we quantified inequity in greenness and park proximity across all urbanized areas in the United States and linked greenness and park access to COVID-19 case rates for ZIP codes in 17 states. Areas with majority persons of colour had both higher case rates and less greenness. Furthermore, when controlling for sociodemographic variables, an increase of 0.1 in the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index was associated with a 4.1% decrease in COVID-19 incidence rates (95% confidence interval: 0.9–6.8%). Across the United States, block groups with lower-income and majority persons of colour are less green and have fewer parks. Our results demonstrate that the communities most impacted by COVID-19 also have the least nature nearby. Given that urban nature is associated with both human health and biodiversity, these results have far-reaching implications both during and beyond the pandemic.
Related data: https://www.sfei.org/data/nature-equity-covid-2021
Related Projects, News, and Events:
 Making Nature's City (Project)
Making Nature's City (Project)
Cities will face many challenges over the coming decades, from adapting to a changing climate to accommodating rapid population growth. A related suite of challenges threatens global biodiversity, resulting in many species facing extinction. While urban planners and conservationists have long treated these issues as distinct, there is growing evidence that cities not only harbor a significant fraction of the world’s biodiversity, but also that they can also be made more livable and resilient for people, plants, and animals through nature-friendly urban design.
 Integrating Planning with Nature (Project)
Integrating Planning with Nature (Project)
Can we gain the benefits of restoring nature while making our cities denser and protecting natural and working lands?
 Google Ecology Advising (Project)
Google Ecology Advising (Project)
SFEI collaborates with the Google Ecology Program to advance the science and application of urban biodiversity and nature-based sustainability planning.
 New article published in Nature Sustainability linking COVID-19 to nature equity, showing communities of color face starkest burden (News)
New article published in Nature Sustainability linking COVID-19 to nature equity, showing communities of color face starkest burden (News)
Erica Spotswood and a team of scientists published pioneering research in Nature Sustainability, finding that COVID-19 tracks neighborhood greenness in the US, exacerbating existing inequity. The study, titled “Nature inequity and higher COVID-19 case rates in less green neighbourhoods in the United States,” demonstrates a fundamental pattern that low-income and majority-minority communities systematically have less access to nature in urban areas across the U.S.
